PREDIS: Pre-disposal management of radioactive waste
The European Commission PREDIS project targets the development and implementation of activities for pre-disposal treatment of radioactive waste streams other than nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste.
It is intended that Member States will profit from measurable benefits including the further development and increase in Technological Readiness Level of treatment and conditioning methodologies for wastes for which no adequate or industrially mature solutions are currently available.
Overview
Project Dates: 1/09/2020 – 31/08/2024
Project Status: Finished
Project Website: predis-h2020.eu/
As society places higher emphasis on environmental stewardship and reduction of waste streams, it is also important that the nuclear community takes efficient management of waste streams as a top priority. In addition, as more legacy waste sites are being cleaned and the nuclear power plant fleet of Europe moves towards decommissioning, there are greater volumes of radioactive wastes to process prior to permanent geological disposal.
The project “PREDIS: Pre-Disposal Management of Radioactive Waste” aims to develop and improve safer treatment and conditioning methodologies and processes for wastes, for which no adequate or industrially-mature solutions are currently available. The project addresses innovation and break-through technologies for better handling of low-level and intermediate level radioactive wastes, with a focus on treatment of metallic materials, liquid organic waste and solid organic waste which can result from nuclear power plant operation, decommissioning and other industrial processes. The project also addresses digitalisation solutions for improved safety and efficiency in handling and assessing cemented-waste packages in extended interim surface storage. An example of this is digital twins and the use of artificial intelligence for big data mining from non-destructive evaluation methods. Through all of these pre-disposal treatment activities, waste acceptance criteria are a critical parameter for optimising the safe and efficient handling and minimisation of wastes over the whole life cycle, from cradle to grave.
PREDIS will produce tools guiding decision-making on the added-value of the developed technologies and their impact on the design, safety, environmental impact and economics of pre-disposal waste management and future disposal. It is anticipated that the project results are close to implementation by the end user community, which is ensured through their active involvement with the partners and the co-funding structure of this EC project. The project’s Strategic Research Agenda will highlight needs for future technology development, investments and needs also from the perspectives of competence development and preservation of knowledge.
With 47 partners from 18 countries across Europe, the 4-year, 24 million euro project, which started 1 September 2020, should make great strides in the best practices and new technologies ready for global markets.
PREDIS is a collaborative project that received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme.
Objective
The PREDIS project develops and increases the Technological Readiness Level of treatment and conditioning methodologies for wastes for which no adequate or industrially mature solutions are currently available, including metallic materials, liquid organic waste and solid organic waste. The PREDIS project also develops innovations in cemented waste handling and pre-disposal storage. The technical Work Packages align with priorities formulated within the Roadmap Theme 2 of EURAD and with those identified by the project’s industrial End Users Group (EUG). PREDIS will produce tools guiding decision-making on the added value of the developed technologies and their impact on the design, safety and economics of waste management and disposal.
PREDIS will liaise with EURAD to provide complementarity on areas including the adaptation and update of the reference founding documents of the European Joint Programme (vision, roadmap, governance and implementation mechanisms), and the organisation of training courses and mobility training schemes to enhance sharing and transfer of knowledge and competence as part of knowledge management activities.
The PREDIS project specifically targets Radioactive Waste Producers (RWP) as a separate group within the radioactive waste management process. The consortium is supported by a End User Group (EUG) representing wide-spread European as well as international interest. PREDIS encompasses the wider European Community, allowing cross-fertilisation and interaction between different national programmes. Numerous dissemination activities, including with Nugenia, IAEA and NEA, will be undertaken to maximise PREDIS’s impact to all the identified stakeholders in the field.
PREDIS high-level objectives are to:
- develop solutions (methods, processes, technologies and demonstrators) for future treatment and conditioning of waste across a number of Member States (MSs) for which no industrially mature or inadequate solutions are currently available, improving safety during next waste management steps;
- improve existing solutions with safer, cheaper or more effective alternative processes where they bring measurable benefits to several MSs;
- analyse criteria, parameters and specifications for materials and packages with associated Waste Acceptance Criteria (WAC) for pre-disposal and disposal activities, supporting homogenisation of waste management processes across Europe.
Work Packages
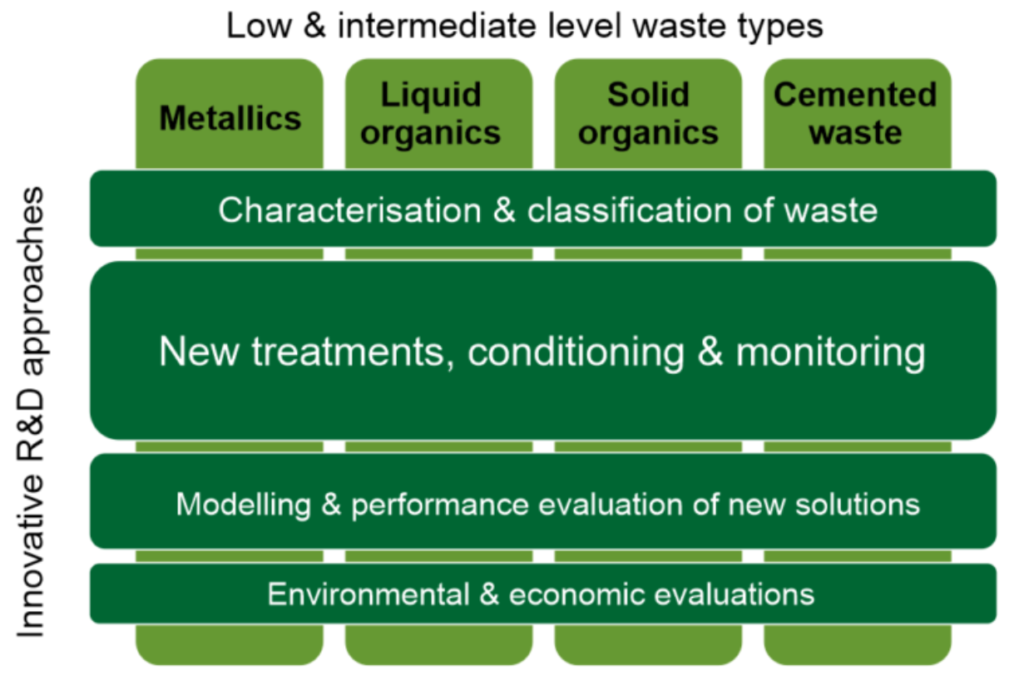
The PREDIS project consists of a strategic, a knowledge management and four technical work packages. Coordinator of the project and leader of Work Package 1 Management and Dissemination is VTT, Finland. The innovative R&D approaches are horizontal over the technical work packages, with strong support of strategic work and training & mobility activities.
WP2 – Strategic Implementation
This work package aims to enhance the strategic implementation of the outputs of this pre-disposal project and focus future pre-disposal collaborative programmes through extensive engagement of stakeholders across member states and international bodies.
The main objectives of WP2:
- Identifying the organisations responsible for waste streams, who have an interest in improving pre-disposal waste management activities, and establishing a wide inclusive pre-disposal ‘user community’ of actors: utilities, nuclear facility operators, decommissioners and waste management organisations. This user group will inform the strategic research agenda throughout the programme.
- Consolidating existing and developing the future Strategic Research Agenda (SRA) in PREDIS, feeding into the EURAD Roadmap (mainly Theme 2).
- Liaison with the EURAD project.
- Characterisation and set of generalised waste acceptance criteria for waste stream issues related with this project in synergy with EURAD WP9 – Routes.
- Establish lifecycle methodologies for systematic environmental and economic evaluation of pre-disposal technologies in the technical work packages and future SRA.
- Implementation of the project results by the end users with radioactive waste producers and waste management organisations.
The updated SRA will allow to structure future work programme priorities (RD&D, Strategic Studies and Knowledge Management) and to visualise progress made where needs are met, thereby improving the overall radioactive waste management process.
WP3 – Knowledge Management
The project provides a high level of training and mobility, aiming for enhanced knowledge and competence transfer between national programmes by enabling cross-fertilisation between experts and scientists from both experienced and developing countries. Over 10% of the budget is dedicated to activities fostering training of next generation experts, both through actual knowledge management actions as well as integrated into the technical activities allocated to PhD students, postdoc students, internships and trainees.
The main objective of Knowledge Management (KM) activities is to develop and transfer knowledge and competence across Member States national programmes, but also to preserve knowledge transfer to coming generations.
The needs for knowledge management differs between the different end-users and stakeholders. Thus, the alignment of the KM objectives with end-users and stakeholders involvement is the driving force of this work package.
To meet these objectives KM activities are focused on:
- Development of a joint Knowledge Management program with EURAD
- State-of-Knowledge (SoK) collection and documentation
- Implementation of Training and Mobility programmes
WP4 – Innovations in metallic material treatment and conditioning
The overall objectives of WP4 are to:
- Minimise through new and/or optimised characterisation, treatment and decontamination processes, the amount of metallic waste to be disposed of in disposal facilities, by allowing more efficient clearance and recycling.
- Contribute to the development of a new reference, stable and safe solution for the storage and final disposal of reactive metallic wastes, such as aluminium and beryllium.
- Estimate the potential scale of opportunity to optimise the management of European metallic wastes, including quantification of the benefits in economic terms and application of the waste hierarchy.
The relevance and need of this work package are directly linked to the currently foreseen end-of-service-life predictions of the current nuclear European fleet, and of the accompanying decommissioning processes, which necessitate the development of more efficient and effective decontamination and remediation methods to minimise the production of wastes and to optimise application of the waste hierarchy through recycling and reuse of materials.
WP5 – Innovations in liquid organic waste treatment and conditioning
The main aim of WP5 is to investigate and develop innovative direct conditioning solutions:
- Implementing geopolymers and related alkali-activated materials as mineral binders
- Fulfilling technical and economic requirements related to RLOW (radioactive liquid organic waste)
- Leading to final waste showing properties and performances compatible with safety and technical requirements related to disposal but also prolonged storage and transport. Disposability assessment and demonstration are key issues and challenges in WP5. In particular, applicability of the direct conditioning route according to RLOW radiological categories (VLLW, LLW/ILW-SL, ILW-LL) and according to disposal facilities features (near-surface and/or intermediate-depth and/or geological) has to be investigated and analysed.
The relevance of WP5 is directly related to the issue of RLOW without management route:
- Societal issue: by targeting a family of waste without a management route, WP5 contributes to a general goal of sustainable management of radioactive waste, limiting the burden to future generations.
- Environmental and nuclear safety issues: the storage of large volumes of RLOW awaiting treatment, over long periods, raises questions about nuclear safety and their potential environmental impact (flammability, toxicity, radiolysis, etc.).
- Technical issues: WP5 aims at developing flexible and versatile innovative solutions that can cover a large part of the spectrum of RLOW without management route at the European scale.
- Industrial and economic issues: the technical solutions developed in WP5 must be acceptable from technical and economic points of view for all actors including WMO and RLOW owners.
WP6 – Innovations in solid organic waste treatment and conditioning
The overall objectives of WP6 are to:
- Demonstrate the reliability of alkaline binders for conditioning of residues and secondary wastes stemming from primary (e.g., thermal) treatment of RSOW (radioactive solid organic waste). The alkaline binders investigated in this project include both (common) cementitious materials and (novel) materials like geopolymers.
- Verify the matrix performance of conditioned final/ultimate waste according to a set of generic waste acceptance criteria (WAC).
- Demonstrate thermal treatment methods leading to a significant volume reduction and to safe reconditioned waste packages, extending the scope already established by the THERAMIN project and closing the waste management cycle.
- Improve understanding of materials inventory eligible to thermal treatment and of the reconditioned wastes once the conversion and immobilisation are achieved. This objective will increase the potential for end users to assess the deployment of results based on their own specific waste streams.
The relevance of WP6 is for radioactive waste producers and waste management organisations, who are faced with low- and intermediate-level radioactive solid organic waste (RSOW) streams for which the current conditioning methods generate waste forms whose safe long-term storage and disposal is difficult to achieve and/or demonstrate. The target is to develop and demonstrate methods/binders that produce sufficiently stable and low reactive waste in the alkaline conditions, and hence could be expected to prevail in many final repositories.
WP7 – Innovations in cemented waste handling and pre-disposal storage
The overall objectives of WP7 are to:
- Compile information about the state of the art of current methods and procedures for cemented waste management with specific focus on monitoring during preparation, handling and long-term storage Identify, evaluate and demonstrate store and package quality assurance (mainly NDE) and monitoring technologies.
- Demonstrate the capability of geochemical and chemo-mechanical models to describe the chemical and mineralogical evolution of cemented waste packages and to demonstrate their suitability for disposal.
- Develop, adapt and demonstrate digital twin technology, methods for data handling and an overall digital decision framework.
- Identify opportunities for increased store automation, reducing human exposure to radiation.
- Identify options for post treatment of packages and potential approaches to improve package design, construction and maintenance.
This work package is relevant to end users aiming to:
- Understand the evolution of waste packages during the extended interim storage periods through store monitoring, package condition monitoring, modelling and decision frameworks, thereby contributing to their future safe handling, transport and acceptance into a final disposal facility.
- Identify packages in need of remedial treatment and options for treatment.
- Automate operation of waste stores using digital and robotics technology.